Use Case Specific Requirements
Authored by:
Treasury Multisigs
Key requirements:
- Allowance module required for all multisigs (see Modules & Guards)
Hot/Cold Wallet Separation
- Hot wallet must be used as an intermediary for treasury wallets
- Cold wallet must store the majority of assets
- Only basic transfers to the hot wallet address allowed
- Hot wallet must have a minimum 2-of-3 signer quorum
Wallet Segregation
- Very high value assets must be distributed amongst separate wallets to prevent potential loss of all assets
- At least 3 equally funded cold wallets is recommended
- Segregated wallets should be managed by different multi-sigs
- Seldom used wallets should have increased time-lock periods
- Any activity on seldom used wallets should trigger alerts to the entire team
External Signer Requirements
- Multi-sigs managing high value wallets and contracts should have at least 1 additional required signer that is external to the organization (such as a security partner or trusted advisor)
External Transaction Monitoring
- A third party outside of the organization should be set up to monitor time locked transactions for anomalies and unintended transaction effects
- The external monitor must perform transaction simulation of all pending transactions
- Monitor reports must be delivered at least 48 business hours before the time lock for a transaction lapses in order to provide adequate time to respond in the event of an anomaly
Emergency response Multisigs
Training & Drills:
- Bi-annual paging system tests to verify alert functionality
- Annual full emergency simulation with all signers
Additional requirements:
- Geographic distribution encouraged for 24/7 coverage
- 24/7 availability for threshold number of signers
Capital allocation Multisigs
Operational constraints:
- Encourage on-chain constraints wherever possible (smart contract limits, parameter bounds)
- Protocol expertise required for all signers
Smart contract control Multisigs
On-chain constraints:
- Timelock contracts for major changes (upgrades, significant parameter changes)
- Parameter limits enforced by smart contracts where feasible
Threshold considerations:
- Higher thresholds for contract upgrades (consider 7/9+)
- Lower thresholds acceptable for highly constrained operations (rate setting with bounds and a backup recovery mechanism to replace the multisig)
Timelock Configuration
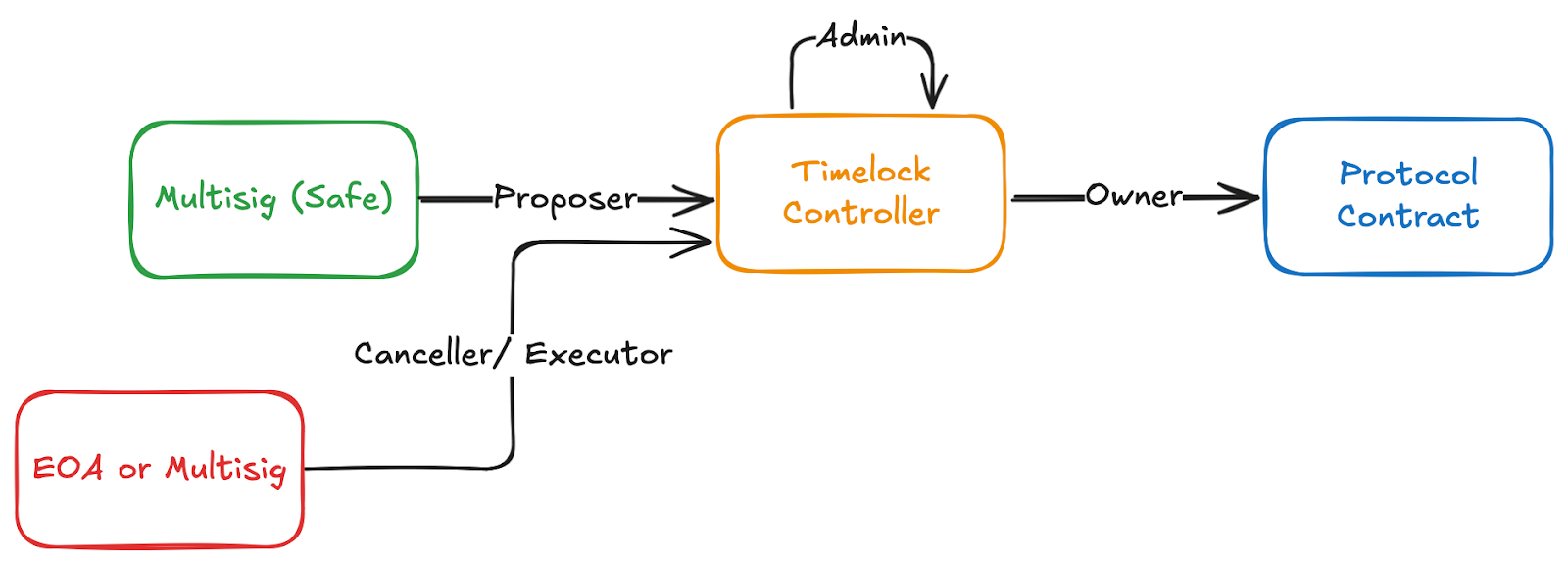
For sensitive protocol operations like configuration changes or upgrades it is recommended to use a timelock contract (eg. OpenZeppelin Timelock Controller) to stage transactions on-chain for final verification before execution. It is not necessary to have a long delay. Some timelock contracts are even configured with 0 delay. The key is to have the full transaction payload fully on chain after signature with a final opportunity to review it and cancel it.
Configuration
When using a timelock contract the timelock address will be set as the owner or role-holder for the protocol contract. The Safe will be the sole contract that has the Proposer role on the timelock contract. The Safe, or an address of a multisig signer, or other desired EOA can be set as the canceller or executor on the timelock contract. By default the timelock contract is set to be its own admin. This means that any changes to timelock contract roles also go through the timelock stage.
Veto Quorum
- Establish a smaller veto group separate from the confirmation quorum to review and confirm transaction legitimacy
- Organizations can establish veto quorums to bypass time-locks in case of emergency
- The standard quorum plus two additional signers should be required to bypass
Recommended Time-Lock Delays
Time-locks should delay transactions a minimum of 3 days.
Simulation Consideration
When using a timelock the simulation for the multisig transaction will not show the execution of the transaction but instead the addition of the pending transaction to the timelock. The pending transaction can be simulated manually as shown in Simulation testing.